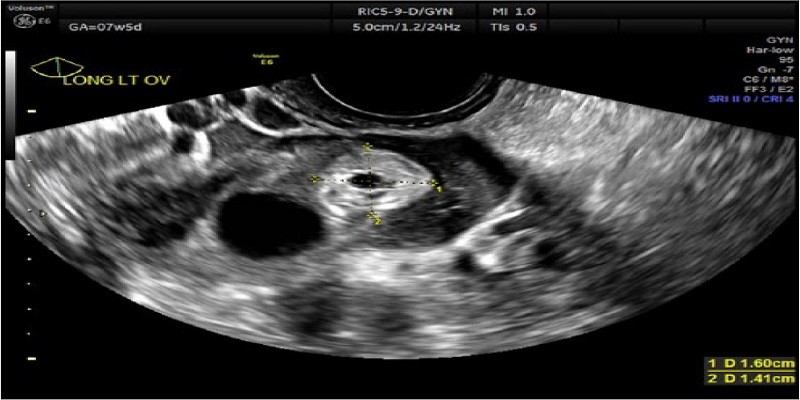
A cyst is a sac-like pocket of tissue that can contain fluid, air, or other substances. Cysts can form anywhere on the body, including the ovaries. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus.
While it’s possible for a cyst to be mistaken for an ectopic pregnancy, there are several key differences between the two conditions. For example, an ectopic pregnancy will usually cause abnormal bleeding from the vagina, whereas a cyst typically does not. Additionally, an ectopic pregnancy can often be detected via ultrasound, whereas a cyst may not be visible on this type of imaging.
If you think you may be experiencing either condition, it’s important to see your doctor right away for further evaluation and treatment.
There are many different types of cysts that can occur in the body, and ovarian cysts are one of the most common. While most ovarian cysts are benign and cause no symptoms, some can be large enough to cause pain or discomfort. In rare cases, an ovarian cyst can rupture, which can lead to serious complications such as bleeding or infection.
Ectopic pregnancy is another condition that can cause similar symptoms to those caused by an ovarian cyst. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg becomes implanted outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This can cause the tube to rupture, which can lead to heavy bleeding and potentially life-threatening complications.
Because both conditions can cause similar symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider if you experience any unusual pelvic pain or bleeding. An ultrasound will usually be able to distinguish between an ovarian cyst and an ectopic pregnancy. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you will need prompt treatment to prevent serious complications.
Ovarian cyst & Ectopic Pregnancy while on implant|| how i almost died
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Mistaken for Ovarian Cyst?
Most ectopic pregnancies occur in the Fallopian tube, but they can also occur in the ovary, cervix, or abdominal cavity. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms on or near the ovary. A pregnancy growing in the ovary may cause an ovarian cyst to form.
However, not all ovarian cysts are due to pregnancy. The most common type of ovarian cyst is called a functional cyst. These usually form during the childbearing years and go away without treatment within a few months.
Rarely, a functional cyst can grow large enough to cause pain or rupture (burst). If you have an ectopic pregnancy, it’s important to get treated right away because this condition can be life-threatening if not treated promptly and properly. If you’re diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy, you’ll likely need surgery to remove the embryo from your Fallopian tube or other location where it has implanted itself.
What Can Be Mistaken for Ectopic Pregnancy?
There are a few conditions that can be mistaken for ectopic pregnancy. One is called a corpus luteal cyst, which is a type of functional cyst that forms on the ovary during the second half of the menstrual cycle. It is usually benign and goes away on its own.
However, it can cause symptoms similar to those of an ectopic pregnancy, such as abdominal pain and bleeding. Another condition that can be confused with an ectopic pregnancy is an ovarian torsion. This occurs when the ovary twists around, cutting off its blood supply.
This can also cause severe abdominal pain and should be treated immediately. Finally, another condition that can mimic an ectopic pregnancy is an early miscarriage. This can also cause abdominal pain and bleeding but typically starts sooner than an ectopic pregnancy would (usually within the first 6 weeks of pregnancy).
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor right away so that they can properly diagnose and treat you.
How Can You Tell the Difference between a Corpus Luteum Cyst And an Ectopic Pregnancy?
When trying to determine if you are experiencing an ectopic pregnancy or a corpus luteum cyst, there are several key factors that can help with diagnosis. One of the most important is whether or not you are experiencing any pain. With an ectopic pregnancy, pain is typically one of the first symptoms and is described as being sharp and concentrated in one specific area.
This pain is caused by the embryo growing outside of the uterus and attaching itself to another organ, which can cause that organ to rupture. In contrast, a corpus luteum cyst generally does not cause any pain at all. Another factor that can be helpful in making a diagnosis is where the pregnancy hormone beta hCG is being produced.
In an ectopic pregnancy, this hormone will usually be present in lower levels than what would be expected for a normal pregnancy because the embryo isn’t developing properly. With a corpus luteum cyst, however, beta hCG levels will usually be within the normal range for early pregnancy since the cyst forms from tissue that normally supports a pregnancy. Ultrasound can also be useful in distinguishing between these two conditions.
An ectopic pregnancy will often show an empty uterus on ultrasound while still detecting high levels of beta hCG in the blood. A corpus luteum cyst, on the other hand, will appear as a fluid-filled sac on ultrasound and won’t typically cause any elevations in beta hCG levels. If you think you may be experiencing either an ectopic pregnancy or a corpus luteum cyst, it’s important to see your doctor right away so they can perform further testing and make sure you receive appropriate treatment.
Can a Cyst Be Mistaken for a Fetus?
There are a few ways that a cyst can be mistaken for a fetus. The most common way is if the cyst is located in the uterus. If an ultrasound is performed, the cyst may appear to be a fetus because it will have a similar shape and size.
Another way that a cyst can be mistaken for a fetus is if it contains fluid and tissue that looks like a baby. This is called a pseudocyst and can occur when the egg does not implant properly in the uterus.

Credit: obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Difference between Ovarian Cyst And Ectopic Pregnancy
There are many different types of cysts that can develop in a woman’s ovaries. The most common type of ovarian cyst is called a functional cyst. These cysts usually form during the childbearing years and are not cancerous.
Functional cysts typically disappear on their own within a few months. Another type of ovarian cyst is called an endometrioid cyst. These cysts can occur at any age and may be cancerous.
Endometrioidcysts contain tissue that looks like the lining of the uterus (endometrium). When this type of tissue grows outside of the uterus, it is called endometriosis. Endometriosis can cause pain and bleeding during menstruation.
It can also make it difficult to become pregnant or may lead to infertility. Surgery is often necessary to remove endometrioidcysts. The third type of ovarian cyst is called a dermoidcyst .
Dermoidcysts are present at birth and contain various types of tissues, including skin, hair, and teeth. Dermoidcysts are usually benign (not cancerous), but they can grow large and cause pain or discomfort. Surgery is often necessary to remove dermoidcysts .
There are also several other less common types of ovarian cysts , including: polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) , which results in multiple small follicles on the ovaries; Meigs’ syndrome , which causes fluid-filled sacs to form on or near the ovaries; and Krukenberg tumors , which arise from cells in the fallopian tubes that have spread to the ovaries . All three conditions can be associated with fertility problems .
Conclusion
Many women worry that they may have an ectopic pregnancy when they find out they have a cyst. However, it is very unlikely that a cyst could be mistaken for an ectopic pregnancy. Cysts are usually benign and don’t pose any threat to the baby.
Last Updated on January 19, 2023 by Marjorie R. Rogers, MA (English), Certified Consultant